Defense
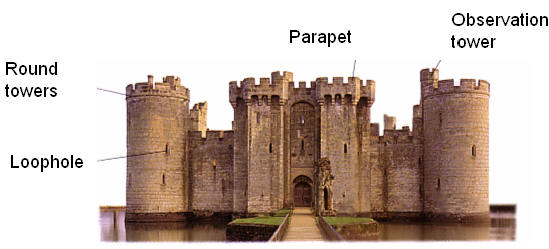
Castles had to be defended in war. The first obstacle a enemy would face was a moat, wet or dry. This was used to stop enemies from getting siege weapons near the castle. One of the other defenses used were machicolated parapets. Men would drop boiling oil, hot water and sand or rocks through the gaps in the floors. Defenders could also shoot from loopholes. These windows are not large enough to be shot into, but can be shot out of.
Lord and Lady
A castle was home to the lord and lady. Some powerful lords may have had several castles and he would appoint a castellan to run the castle in his absense. The families of knights may also live in the castle and children of other lords may also have been trained there.
Servants
These were some of many people living in the castle:
Nurses- Take full care of infants of the lord and lady.
Domestic Servants- Servants who mainly performed specific tasks, including weavers, carpenters, and gong farmers (people who emptied the pit under each toilet)
Ladies-in-waiting- Well educated woman who acted as attendants to the lords family.
Kitchen Staff- These were mainly men and did jobs such as cooking, baking, serving food, making wine, making beer and taking care of the wine cellar.
Outside servants- These included stable grooms, blacksmiths and huntsmen. Huntsman ranged from warreners (for hunting rabbits) to falconers (using a falcon to catch animals).
Dungeon
A castle was also used as a dungeon. Some prisoners were rich or important and were imprisoned so as to get a large ransom. Some prisoners were enemies of the lord. Prisoners would mainly be treated well because they were worthless dead. They may give their word of honor not to escape, in return for some freedom.